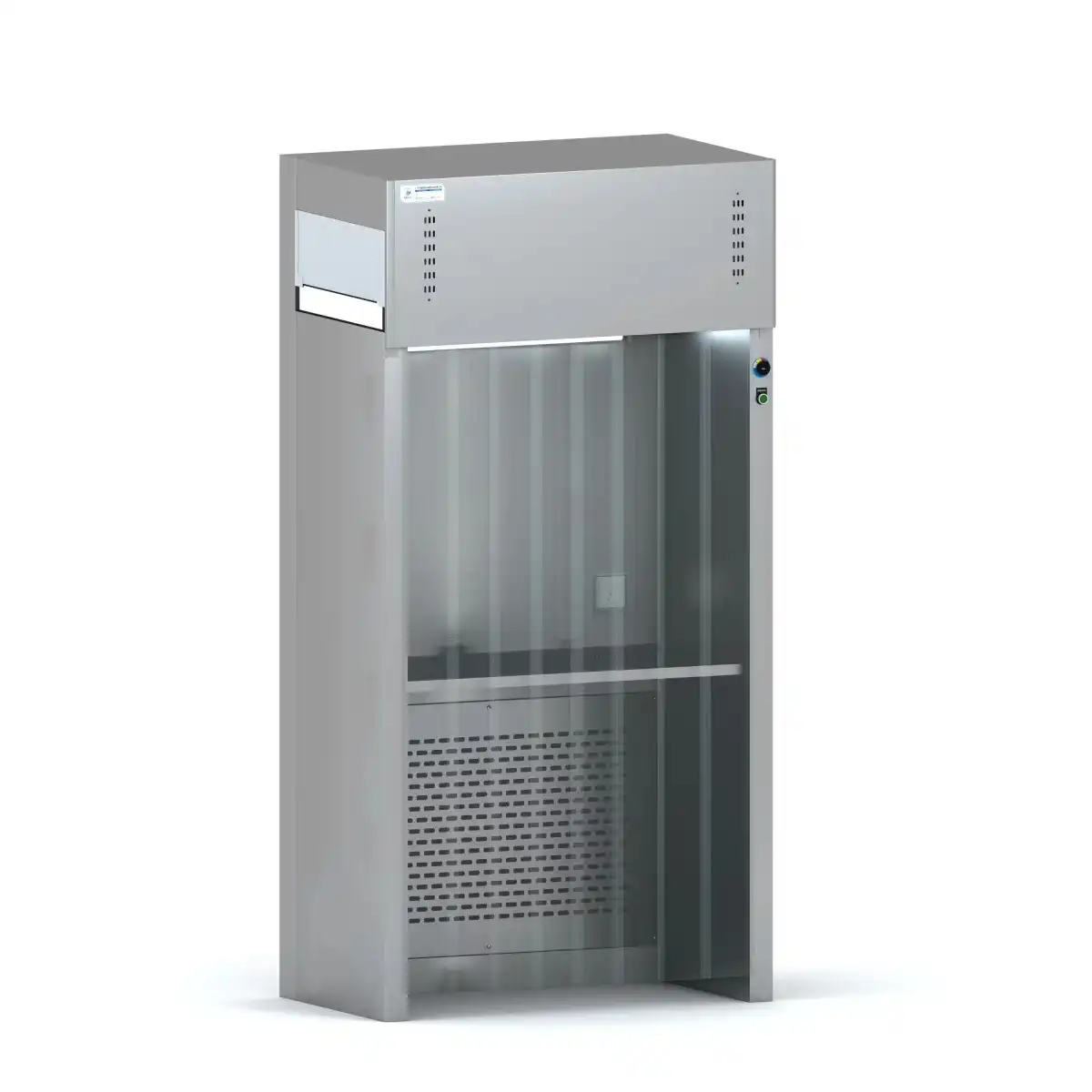
Where are fume extraction hoods used?
2025-05-09 15:47:29
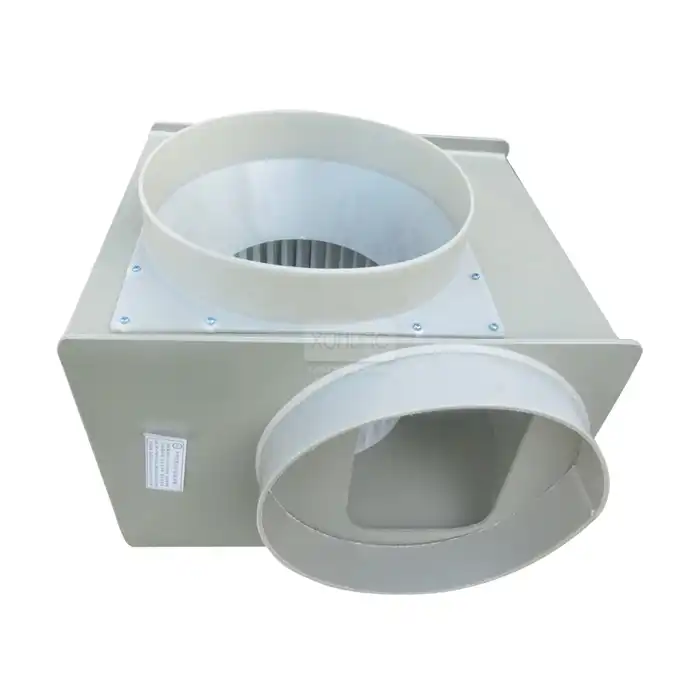
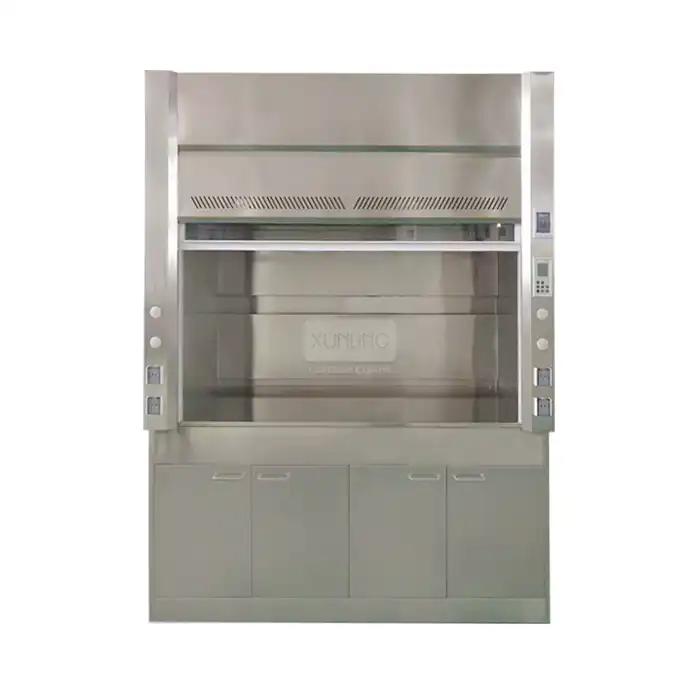
Fume extraction hoods are essential safety equipment in various industries and environments where hazardous or noxious gases, vapors, fumes, dust, and other airborne contaminants are generated during processes and operations. These specialized ventilation systems are designed to capture, contain, and remove harmful substances at their source, protecting workers and researchers from exposure to potentially dangerous materials. Fume extraction hoods create a controlled airflow that draws contaminated air away from the work area and filters or exhausts it safely outside, maintaining a clean and safe working environment. They are critical components in laboratories, industrial facilities, medical institutions, educational settings, and research centers where chemical, biological, or particulate hazards are present.
Industries That Rely on Fume Extraction Hoods
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
The chemical and pharmaceutical industries utilize fume extraction hoods extensively during their research, development, and manufacturing processes. In chemical laboratories, scientists often work with volatile organic compounds (VOCs), acids, bases, and other reactive substances that can release harmful vapors. Fume extraction hoods provide a controlled environment where these reactions can be safely conducted without endangering the laboratory personnel. The pharmaceutical industry, in particular, requires stringent containment measures during drug development and production. Potent active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) must be handled in enclosed environments to prevent cross-contamination and protect workers from exposure to potentially toxic compounds. Fume extraction hoods with HEPA filtration systems are commonly employed in Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) facilities to maintain clean room conditions while safely removing airborne contaminants. Additionally, quality control laboratories in pharmaceutical companies rely on fume extraction hoods for analytical procedures involving solvents and reagents that might pose health risks through inhalation or skin contact. These specialized ventilation systems are essential components in maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and occupational health and safety standards in these industries.
Educational Institutions and Research Laboratories
Educational institutions and research laboratories are major users of fume extraction hoods for both teaching and cutting-edge scientific investigations. In university chemistry, biology, and engineering departments, fume extraction hoods are fundamental to undergraduate and graduate teaching laboratories where students perform experiments with various chemicals and materials. These controlled environments allow students to safely gain hands-on experience while minimizing exposure to hazardous substances. Research laboratories conducting fundamental and applied scientific investigations often work with specialized materials, including nanomaterials, reactive compounds, and biological specimens that require proper containment. Advanced research frequently involves custom experimental setups that would be unsafe without appropriate ventilation controls. Fume extraction hoods in these settings are often equipped with special features such as wash-down systems, explosion-proof components, or specialized filtration based on the specific research requirements. Additionally, core research facilities offering shared instrumentation and analytical services across disciplines typically house sensitive equipment within fume extraction hoods to protect both the instruments and users from chemical exposures while maintaining clean operating conditions. These educational and research applications of fume extraction hoods help cultivate a culture of laboratory safety while enabling scientific advancement and discovery without compromising personnel health.
Medical and Healthcare Facilities
Medical and healthcare facilities employ fume extraction hoods across various departments where protection from airborne hazards is critical. In hospital pharmacies, specially designed laminar flow fume extraction hoods are used for the compounding of hazardous drugs, including chemotherapy agents and other cytotoxic medications. These hoods prevent the aerosolization of drug particles that could be inhaled by pharmacy staff during medication preparation. Pathology and histology laboratories utilize fume extraction hoods when working with preservation chemicals, stains, and fixatives such as formaldehyde and xylene, which are known respiratory irritants and potential carcinogens. The fume extraction hoods in these settings ensure that technicians can safely process tissue samples without exposure to harmful fumes. Diagnostic laboratories performing various clinical tests also benefit from fume extraction hood technology when carrying out procedures involving volatile reagents. Additionally, biomedical research facilities within healthcare institutions use specialized fume extraction hoods for work involving infectious agents, requiring biosafety features beyond standard chemical protection. Many modern medical fume extraction hoods are equipped with specialized filtration systems that not only protect workers but also prevent the release of potentially harmful substances into the environment, aligning with healthcare sustainability initiatives and regulatory compliance requirements. These applications demonstrate the crucial role fume extraction hoods play in maintaining safety standards across diverse medical and healthcare environments.
Applications in Specialized Industries
Electronics Manufacturing and Semiconductor Production
The electronics manufacturing and semiconductor production industries require pristine working environments with exceptional contamination control, making specialized fume extraction hoods indispensable in these sectors. During printed circuit board (PCB) assembly, soldering processes release potentially harmful fumes containing lead, flux residues, and other volatile compounds that must be efficiently captured and removed by fume extraction hoods equipped with particulate and chemical filtration capabilities. Semiconductor fabrication involves numerous processes utilizing aggressive chemicals, including hydrofluoric acid, sulfuric acid, and various cleaning solvents that pose significant health hazards if not properly contained. Clean room compatible fume extraction hoods with laminar flow systems prevent both operator exposure and cross-contamination of sensitive electronic components. In advanced electronics manufacturing, nanotechnology applications require handling of extremely fine particles that must be contained and filtered through specialized extraction systems to prevent inhalation of potentially harmful nanoparticles. Many electronics manufacturing facilities utilize ductless fume extraction hoods with advanced molecular filtration media that allow for flexibility in production floor layout while maintaining stringent air quality standards. These specialized extraction systems not only protect workers but also safeguard the integrity of delicate electronic components and devices that could be damaged by airborne contaminants, making them critical infrastructure in maintaining both personnel safety and product quality in high-technology manufacturing environments.
Automotive and Industrial Manufacturing
The automotive and industrial manufacturing sectors employ fume extraction hoods for numerous applications involving hazardous materials and processes that generate airborne contaminants. During automotive paint preparation and application, workers mix and apply various primers, paints, and clear coats containing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and isocyanates that require effective capture and removal through specially designed spray booth fume extraction systems. Battery production facilities, particularly those manufacturing lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles, utilize fume extraction hoods during electrode preparation, electrolyte filling, and testing to control exposure to solvents, electrolyte vapors, and potentially hazardous decomposition products. Industrial adhesive applications, common in both automotive and general manufacturing, often involve epoxies, cyanoacrylates, and solvent-based adhesives that release fumes requiring controlled ventilation through appropriate extraction systems. Metal fabrication processes such as welding, laser cutting, and plasma cutting generate metal fumes, particulates, and gases that are captured by specialized extraction hoods positioned near the operation to prevent respiratory exposure to potentially harmful metal-containing aerosols. Many modern manufacturing facilities integrate fume extraction hoods directly into production lines, with customized designs that accommodate specific equipment configurations while maintaining effective capture of process-generated contaminants. These applications demonstrate how fume extraction hoods have evolved beyond traditional laboratory settings to become essential safety equipment in diverse manufacturing environments where worker protection and environmental compliance are paramount concerns.
Art Conservation and Restoration
Art conservation and restoration laboratories use specialized fume extraction hoods to protect conservators working with a variety of solvents, adhesives, and chemical treatments required for the preservation of cultural heritage materials. During painting restoration, conservators often apply cleaning solutions, varnish removers, and consolidants containing petroleum distillates, alcohols, ketones, and other volatile organic compounds that require effective containment and removal through appropriate extraction systems. Document and paper conservation processes frequently involve bleaching agents, deacidification chemicals, and adhesive solvents that can release harmful vapors, necessitating the use of specialized horizontal flow fume extraction hoods designed to accommodate flat artifacts while providing operator protection. Archaeological conservation laboratories utilize fume extraction hoods when treating artifacts with preservatives, cleaning agents, and consolidants, particularly when working with metal objects that may require acidic treatments or corrosion inhibitors. Many art conservation facilities employ ductless fume extraction hoods with specialized carbon filtration media specifically designed to capture the unique range of solvents used in conservation treatments while allowing the hood to be positioned in historic buildings where ducted systems might not be feasible. Additionally, conservation science laboratories performing analytical work on artistic materials benefit from fume extraction hoods when conducting tests involving chemical reagents or sample preparation techniques that generate potentially harmful vapors. These specialized applications demonstrate how fume extraction hoods have been adapted to meet the unique requirements of cultural heritage preservation while maintaining the highest standards of conservator safety and artifact protection.
Environmental and Safety Considerations Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Regulatory compliance and adherence to established standards govern the implementation and operation of fume extraction hoods across various industries. Organizations such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) in the United States establish permissible exposure limits (PELs) for numerous chemical substances, requiring employers to implement engineering controls like fume extraction hoods to maintain workplace exposures below these regulatory thresholds. The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) jointly publish ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 110, which provides standardized methods for testing the performance of laboratory fume extraction hoods, ensuring they meet minimum containment requirements before being certified for use. International standards such as EN 14175 in Europe provide comprehensive guidelines for the safety and performance testing of fume extraction hoods, creating harmonized requirements across member countries. These standards typically address face velocity requirements, containment efficiency, airflow patterns, and alarm systems necessary for safe operation. Healthcare facilities must comply with additional standards such as those published by the United States Pharmacopeia (USP) for handling hazardous drugs, which specify requirements for engineered containment devices including fume extraction hoods. Manufacturers of fume extraction hoods must design their products to meet these various regulatory requirements while providing documentation and testing protocols that allow end users to verify ongoing compliance through regular performance testing and certification. Understanding these regulatory frameworks is essential for facilities managers, safety officers, and laboratory personnel responsible for selecting, installing, and maintaining appropriate fume extraction hood systems that ensure worker protection while meeting industry-specific compliance requirements.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability Considerations
Energy efficiency and sustainability have become increasingly important considerations in the design, selection, and operation of fume extraction hoods as organizations seek to reduce their environmental footprint and operating costs. Traditional ducted fume extraction hoods consume significant amounts of conditioned air, requiring energy-intensive makeup air systems to replace exhausted air and maintain building pressure relationships. Modern low-flow and high-efficiency fume extraction hood designs incorporate aerodynamic features, sash configurations, and airflow controls that maintain effective containment while reducing air volume requirements by up to 50% compared to conventional models. Variable air volume (VAV) control systems automatically adjust exhaust rates based on sash position or occupancy detection, providing significant energy savings during periods when the hood is closed or not in active use while maintaining safe operation. Heat recovery systems are increasingly being integrated with fume extraction hood exhaust systems to capture thermal energy that would otherwise be wasted, transferring it to incoming makeup air and reducing heating and cooling energy requirements. Ductless recirculating fume extraction hoods with advanced filtration technology offer an alternative approach to energy conservation by eliminating the need to exhaust conditioned air, though they require careful consideration of appropriate applications and rigorous filter maintenance programs. Many organizations now incorporate life cycle assessment and total cost of ownership analyses when evaluating fume extraction hood options, considering not only initial purchase price but also long-term energy consumption, maintenance requirements, and potential for LEED or other green building certification credits. These energy efficiency strategies not only reduce operational costs but also contribute to institutional sustainability goals and corporate social responsibility initiatives while maintaining the primary function of protecting personnel from exposure to hazardous substances.
Maintenance and Performance Testing
Regular maintenance and performance testing are critical aspects of fume extraction hood operation that ensure continued effectiveness and safety throughout the equipment's service life. Face velocity testing using calibrated anemometers is typically performed at least annually to verify that airflow at the hood opening meets specified parameters, typically 80-120 feet per minute depending on the application and organizational requirements. ASHRAE 110 containment testing uses tracer gas techniques to quantitatively evaluate a fume extraction hood's ability to prevent contaminant escape under various operating conditions, including static tests and dynamic tests that simulate operator movements. Visual airflow verification using smoke or other visualization techniques allows users to observe airflow patterns and identify potential areas of turbulence or reverse flow that might compromise containment performance. Filtration systems in ductless fume extraction hoods require particular attention, with regular monitoring of filter loading, breakthrough detection, and replacement schedules based on usage patterns and types of chemicals handled. Mechanical components including fans, motors, dampers, and control systems must be inspected regularly for signs of wear, corrosion, or malfunction that could impact performance or create safety hazards. Certification programs typically require documentation of these various tests and maintenance activities, with records maintained for regulatory compliance and quality assurance purposes. Many modern fume extraction hoods incorporate continuous monitoring systems that provide real-time feedback on airflow parameters, allowing users to verify proper operation before beginning work and alerting them to potential problems. These comprehensive maintenance and testing regimens ensure that fume extraction hoods continue to provide the expected level of protection throughout their operational life, preventing exposures that could result from degraded performance or undetected failures in critical components.
Conclusion
Fume extraction hoods play a vital role across diverse industries where worker safety and environmental protection are paramount concerns. From chemical laboratories and pharmaceutical manufacturing to educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and specialized industrial applications, these essential engineering controls provide the first line of defense against exposure to hazardous airborne contaminants. As technology advances and regulatory requirements evolve, fume extraction hood systems continue to improve in terms of performance, energy efficiency, and integration with building systems.
Are you looking for high-quality, reliable fume extraction hoods for your laboratory or industrial facility? Xi'an Xunling Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. offers cost-effective solutions with exceptional performance and durability. Our products feature user-friendly designs, backed by comprehensive 5-year warranty and excellent after-sales support. As a professional manufacturer with OEM capabilities and five production bases across China, we deliver custom-made solutions within just 5 days. Ready to enhance your workspace safety with our state-of-the-art fume extraction hoods? Contact our team today at xalabfurniture@163.com and experience the difference that quality engineering makes!
References
1. Johnson, A.E., & Thompson, R.B. (2023). Laboratory Safety Equipment: Standards and Applications for Fume Extraction Hoods. Journal of Chemical Health and Safety, 30(2), 112-125.
2. Williams, S.K., & Chen, H. (2022). Energy Efficiency in Laboratory Ventilation Systems: Modern Approaches to Fume Hood Design. Building and Environment, 198, 107-118.
3. Patel, M.S., Ahmed, K., & Roberts, D.N. (2023). Industrial Applications of Extraction Technologies for Worker Protection. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 84(3), 215-228.
4. Martinez, C., & Yoshida, T. (2021). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Containment Strategies: Implementing Effective Fume Extraction Hood Systems. Pharmaceutical Engineering, 41(4), 32-41.
5. Ramirez, J.L., & Wong, K.H. (2022). Performance Testing Methodologies for Laboratory Ventilation Systems and Fume Extraction Hoods. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, 19(5), 312-325.
6. Thompson, V.S., & Lee, P.Q. (2023). Sustainability in Laboratory Design: Balancing Safety and Environmental Impact of Fume Extraction Hood Systems. Journal of Green Building, 18(2), 145-159.
YOU MAY LIKE