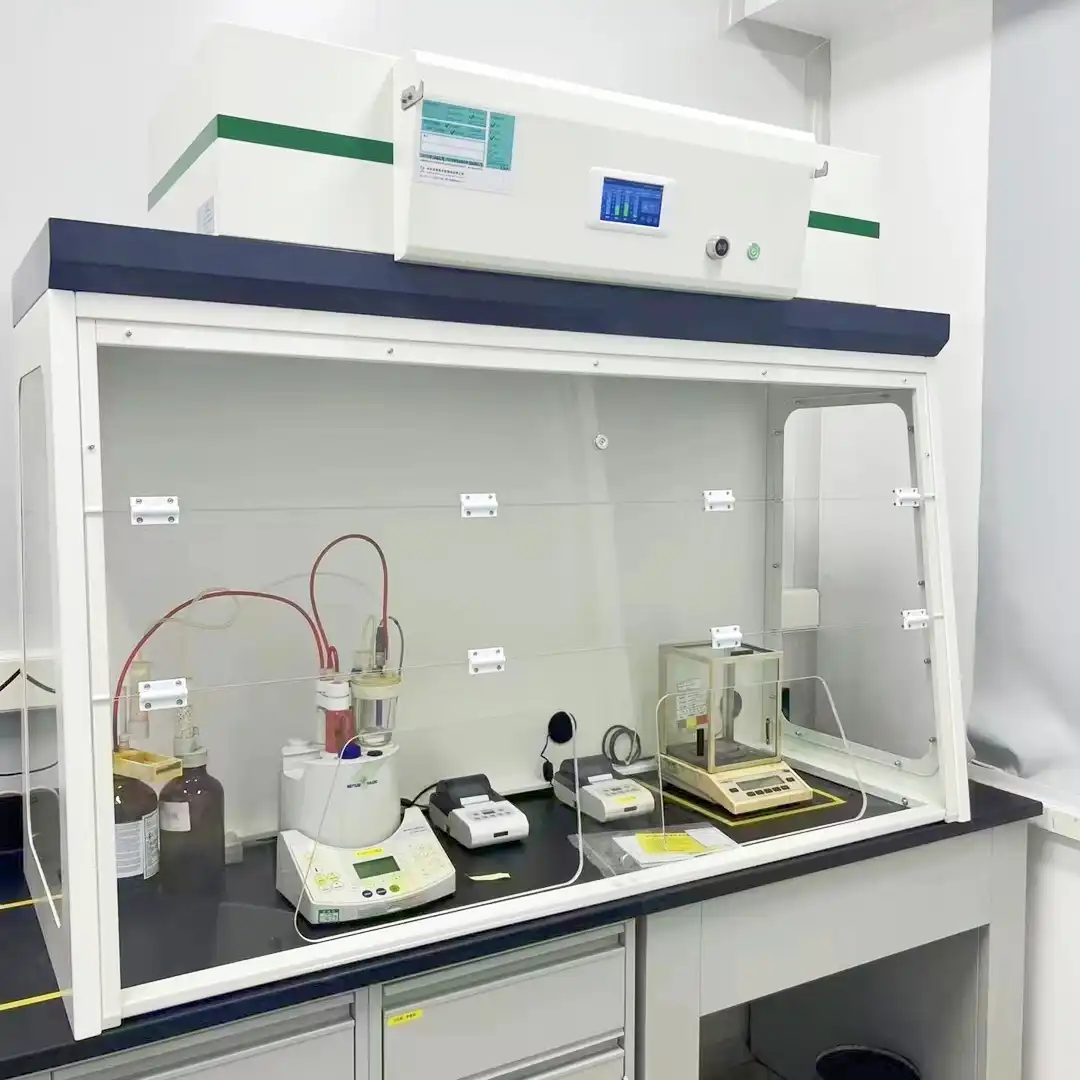
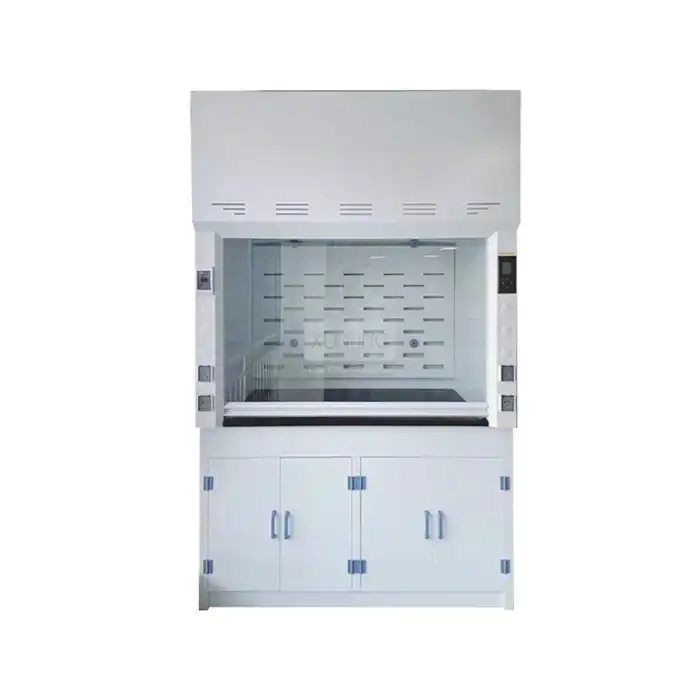
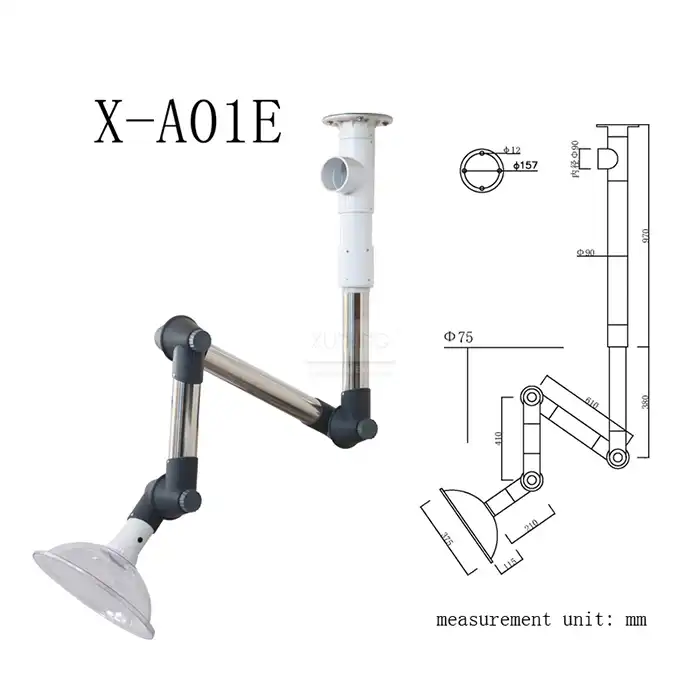
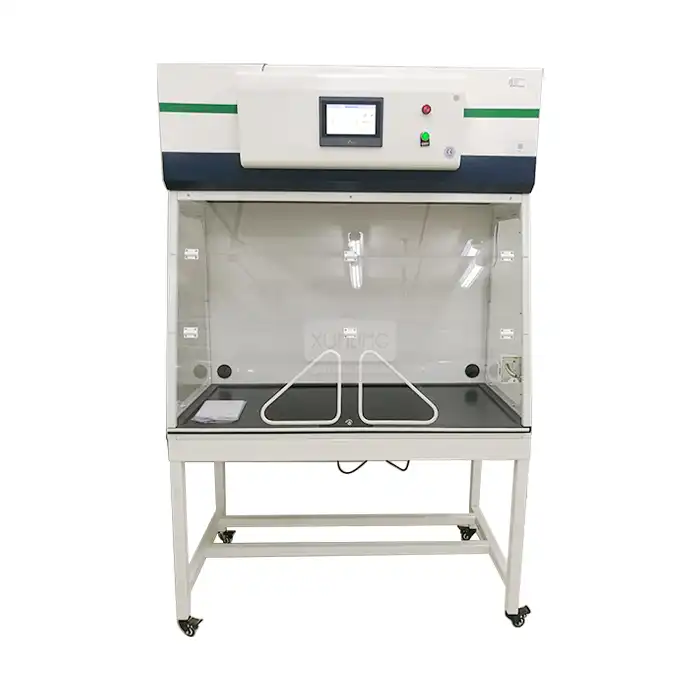
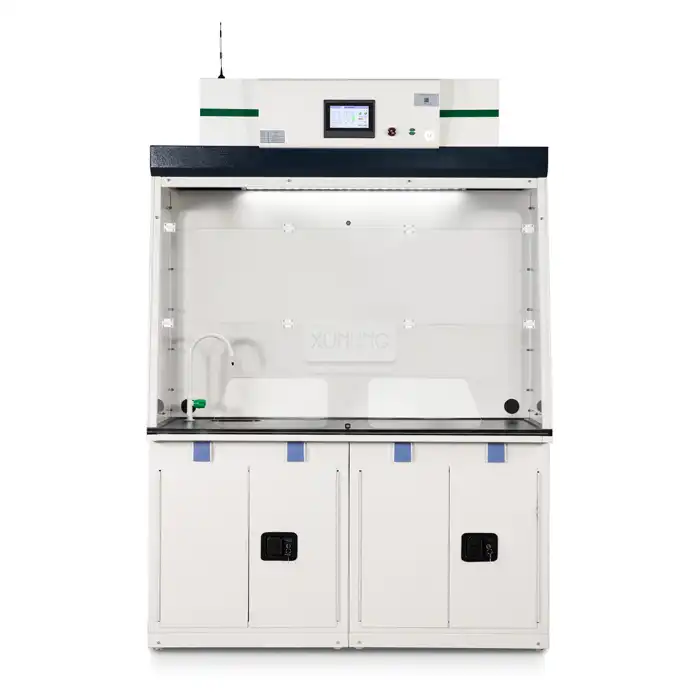
Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber: Complete Buyer's Guide
2025-10-03 09:00:02
Laboratory safety remains paramount in modern research facilities, and selecting the right ventilation equipment can make the difference between a secure working environment and potential hazards. Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber with built-in scrubbers represent a revolutionary advancement in laboratory safety technology, combining traditional fume extraction capabilities with integrated scrubbing systems that neutralize harmful chemicals before they enter the atmosphere. These sophisticated systems offer unparalleled protection for laboratory personnel while ensuring environmental compliance and operational efficiency. Understanding the complexities of these systems is essential for making informed purchasing decisions that will serve your laboratory's needs for years to come.
Understanding Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber Technology
Advanced Scrubbing Mechanisms and Chemical Neutralization
Lab fume hoods with built-in scrubbers utilize sophisticated chemical neutralization processes that go far beyond conventional exhaust systems. These units incorporate wet scrubbing technology, where contaminated air passes through a liquid medium specifically designed to neutralize hazardous compounds. The scrubbing process involves multiple stages: initial contact between contaminated air and the scrubbing solution, chemical reaction and neutralization, and final separation of treated air from the liquid medium. The effectiveness of this system depends on factors such as contact time, scrubbing solution concentration, and flow dynamics. Modern lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems achieve neutralization rates exceeding 95% for most common laboratory chemicals, including acids, bases, and organic solvents. The scrubbing media can be customized based on specific chemical applications, with options including water-based solutions for general applications and specialized chemical solutions for targeted neutralization of specific compounds.
Integrated Design Benefits and System Efficiency
The integration of scrubbing technology directly into the fume hood structure provides numerous operational advantages that traditional separate systems cannot match. This unified design eliminates the need for external scrubbing towers, reducing installation complexity and space requirements while maintaining optimal performance. The lab fume hood with builtin scrubber configuration ensures consistent airflow patterns and prevents dead zones that could compromise safety. Internal sensors monitor scrubbing solution levels, pH, and effectiveness, providing real-time feedback to operators and maintenance personnel. The compact design reduces energy consumption by optimizing air movement patterns and eliminating lengthy ductwork runs. Additionally, the integrated approach allows for precise control of scrubbing parameters, including solution flow rates, contact time, and neutralization efficiency, ensuring optimal performance across varying chemical loads and operational conditions.
Environmental Compliance and Regulatory Standards
Modern laboratory operations must comply with increasingly stringent environmental regulations, making the environmental benefits of lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems particularly valuable. These systems significantly reduce or eliminate the release of hazardous compounds into the atmosphere, helping facilities meet EPA requirements and local air quality standards. The scrubbing process converts harmful vapors into neutralized liquid waste, which can be treated and disposed of through established protocols. Compliance with standards such as ASHRAE 110-95 ensures that these systems meet rigorous performance criteria for containment and safety. The built-in monitoring capabilities provide documentation necessary for regulatory reporting, including emission levels, neutralization efficiency, and maintenance records. Many facilities find that investing in lab fume hood with builtin scrubber technology helps them exceed environmental standards while reducing long-term compliance costs and regulatory risks.
Key Selection Criteria and Performance Specifications
Airflow Dynamics and Containment Performance
Selecting the appropriate lab fume hood with builtin scrubber requires careful consideration of airflow specifications and containment performance characteristics. Optimal airflow velocity typically ranges from 0.3 to 0.6 m/s at the face opening, providing sufficient capture while avoiding turbulence that could compromise containment. The internal airflow design must account for the additional resistance created by the scrubbing system while maintaining uniform velocity profiles across the work surface. Face velocity monitoring systems ensure consistent performance and alert operators to potential issues that could affect containment. The relationship between scrubbing efficiency and airflow rate is critical, as insufficient contact time reduces neutralization effectiveness while excessive flow rates can overwhelm the scrubbing system. Modern lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems incorporate variable airflow control that adjusts based on sash position and operational requirements, optimizing both safety and energy efficiency. Advanced computational fluid dynamics modeling during the design phase ensures optimal airflow patterns that maximize both containment and scrubbing effectiveness.
Construction Materials and Chemical Resistance
The harsh chemical environment within Laboratory Fume Hoods demands materials that can withstand prolonged exposure to corrosive substances while maintaining structural integrity and performance. Lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems typically utilize epoxy resin and polypropylene construction for superior chemical resistance and durability. Epoxy resin surfaces provide excellent resistance to most laboratory chemicals while offering easy cleaning and maintenance. Polypropylene components, particularly in areas directly exposed to scrubbing solutions, offer exceptional resistance to acids, bases, and solvents while maintaining flexibility and impact resistance. The selection of appropriate materials depends on the specific chemicals used in the laboratory, with some applications requiring specialized coatings or alternative materials for optimal performance. Internal components exposed to scrubbing solutions must be manufactured from materials that resist both chemical attack and erosion from liquid flow. Quality lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems incorporate corrosion-resistant hardware, including stainless steel fasteners and specialized gaskets that maintain seal integrity over extended periods.
Size Configurations and Workspace Requirements
Determining the appropriate size for a lab fume hood with builtin scrubber involves balancing workspace requirements with available laboratory space and airflow capacity. Standard configurations include 1200mm, 1500mm, and 1800mm widths, each designed to accommodate different experimental setups and equipment requirements. The internal dimensions must provide adequate space for experimental apparatus while maintaining proper airflow patterns and operator access. Work surface depth affects both containment effectiveness and user ergonomics, with deeper units providing better containment but potentially creating reach difficulties for operators. Height considerations include both the overall unit height and the internal working height, which must accommodate experimental equipment while maintaining proper airflow characteristics. The relationship between external and internal dimensions affects both shipping and installation requirements, particularly in facilities with limited access or ceiling height restrictions. Proper sizing of lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems ensures optimal performance while maximizing available workspace and maintaining user comfort during extended operations.
Installation, Maintenance, and Operational Considerations
Installation Requirements and Infrastructure Integration
The installation of lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems requires careful planning and coordination to ensure optimal performance and compliance with safety standards. Unlike traditional fume hoods that require extensive ductwork connections to remote exhaust systems, these integrated units simplify installation requirements while still demanding attention to specific infrastructure needs. Electrical requirements include not only standard fume hood controls but also power for scrubbing pumps, monitoring systems, and solution circulation equipment. Plumbing connections must accommodate both scrubbing solution supply and waste discharge, with proper sizing to handle peak flow rates and emergency situations. The reduced ductwork requirements of lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems allow for more flexible installation locations while still requiring adequate clearances for service access and emergency procedures. Foundation requirements must account for the additional weight of scrubbing solutions and associated equipment, particularly for larger units or those with extended solution reservoirs. Professional installation ensures proper commissioning, including airflow verification, scrubbing system calibration, and integration with building management systems.
Maintenance Protocols and System Longevity
Effective maintenance protocols are essential for ensuring continued performance and safety of lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems throughout their operational lifecycle. Regular maintenance tasks include monitoring scrubbing solution levels and concentration, inspecting internal components for wear or corrosion, and verifying airflow performance and containment effectiveness. The accessibility of internal components significantly impacts maintenance efficiency, with well-designed lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems providing easy access to pumps, sensors, and solution reservoirs without compromising containment or safety. Scrubbing solution replacement schedules depend on usage patterns and chemical loads, with monitoring systems providing guidance on optimal replacement intervals. Preventive maintenance programs should include regular inspection of seals, gaskets, and moving components to prevent failures that could compromise safety or performance. The integration of diagnostic systems in modern units provides early warning of potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance that minimizes downtime and extends equipment life. Documentation of maintenance activities is crucial for regulatory compliance and warranty requirements, with many systems providing automated logging of service activities and performance parameters.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Analysis
The operational efficiency of lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems extends beyond initial purchase price to encompass long-term operational costs and performance benefits. Energy consumption analysis must consider both the electrical requirements of scrubbing systems and the reduced exhaust fan requirements compared to traditional high-volume exhaust systems. The elimination of extensive ductwork reduces both installation costs and ongoing maintenance requirements while improving overall system efficiency. Scrubbing solution costs vary based on chemical usage patterns and neutralization requirements, with many facilities finding significant cost savings compared to alternative waste treatment methods. The contained nature of lab fume hood with builtin scrubber systems reduces heating and cooling losses compared to traditional exhaust systems, providing additional energy savings in climate-controlled laboratories. Labour costs associated with maintenance and monitoring are generally reduced due to the integrated design and automated monitoring capabilities. Long-term cost analysis should include factors such as regulatory compliance costs, waste disposal expenses, and potential productivity improvements from enhanced safety and reliability.
Conclusion
Lab fume hoods with built-in scrubbers represent a significant advancement in laboratory safety technology, offering comprehensive protection while addressing environmental concerns and operational efficiency. The integration of scrubbing technology with traditional fume hood design creates systems that neutralize hazardous chemicals at the source, reducing environmental impact and regulatory compliance challenges. Xi'an Xunling Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. has established itself as a leading manufacturer in this specialized field, leveraging over 1,100 employees and advanced manufacturing capabilities to deliver reliable, innovative solutions for laboratories worldwide.
Ready to enhance your laboratory safety with cutting-edge technology? As a premier China Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber factory, Xi'an Xunling Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. offers unmatched expertise as your trusted China Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber supplier. Our reputation as a leading China Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber manufacturer stems from our commitment to quality and innovation, while our China Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber wholesale options provide exceptional value for multi-unit installations. Explore our comprehensive range of Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber for sale, featuring competitive Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber price points without compromising on quality. Each High Quality Lab Fume Hood With Builtin Scrubber unit comes with our 5-year warranty, 5-day delivery promise, and comprehensive one-stop service solution. Contact our expert team today at xalabfurniture@163.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our custom-made solutions can transform your laboratory environment into a safer, more efficient workspace.
References
1. American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers. "Method of Testing Performance of Laboratory Fume Hoods." ASHRAE Standard 110-95. Atlanta: ASHRAE, 1995.
2. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. "Criteria for a Recommended Standard: Occupational Exposure to Laboratory Chemicals." DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No. 78-127. Cincinnati: NIOSH, 1978.
3. Laboratory Safety Institute. "Guidelines for Laboratory Ventilation Systems." Journal of Chemical Health and Safety, vol. 12, no. 3, 2005, pp. 15-23.
4. International Organization for Standardization. "Laboratory Equipment - Fume Cupboards - Part 1: Terms and Definitions, Classification and Performance Requirements." ISO 14175-1:2005. Geneva: ISO, 2005.
YOU MAY LIKE









_1756092462006.jpg)