Are mobile fume hoods as effective as fixed ones?
2025-06-12 11:14:36
Laboratory safety is a critical concern for researchers, technicians, and facility managers across various industries. Among the essential safety equipment, Fume Hoods play a pivotal role in protecting personnel from hazardous fumes, vapors, and particles. As laboratory needs evolve, the question of whether mobile fume hoods can match the effectiveness of their fixed counterparts has become increasingly relevant. This comprehensive analysis explores the comparative effectiveness of mobile fume hoods versus traditional fixed installations, considering multiple factors that influence performance, safety, and practicality.
Mobile fume hoods offer comparable effectiveness to fixed fume hoods when properly designed and used within their operational parameters. While fixed fume hoods typically provide higher airflow capacity and more robust containment for highly hazardous applications, mobile fume hoods excel in flexibility, space optimization, and adaptability to changing laboratory layouts. The effectiveness of a mobile fume hood depends on several factors including its engineering design, filtration system quality, maintenance protocols, and adherence to proper usage guidelines. For applications involving moderate chemical usage or specific isolated tasks, mobile fume hoods can provide equivalent protection when equipped with appropriate filtration technology and operated according to manufacturer specifications.
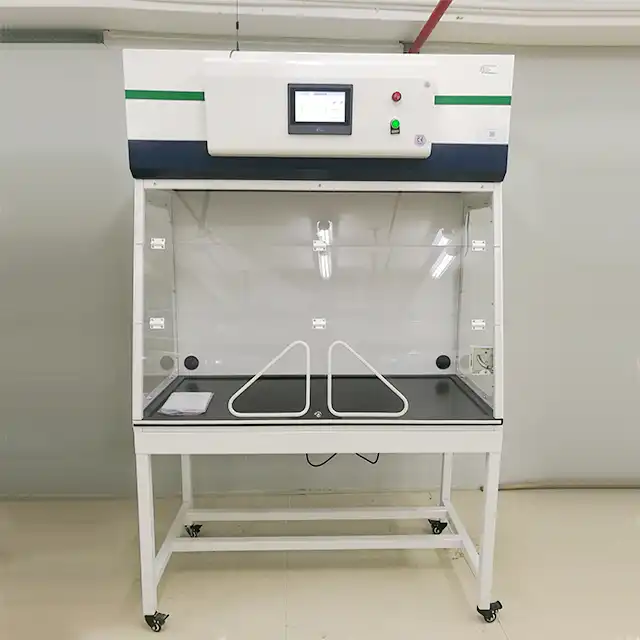

Comparative Analysis of Mobile and Fixed Fume Hood Performance
Engineering Design Differences
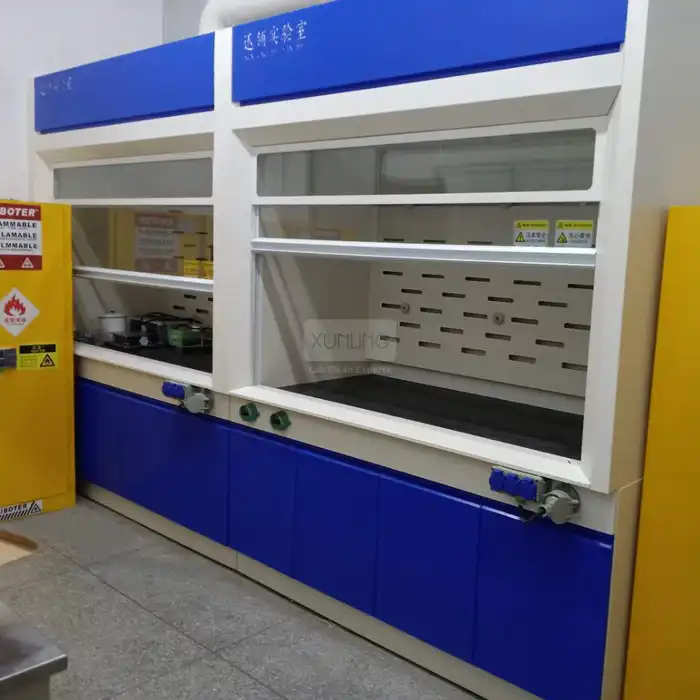
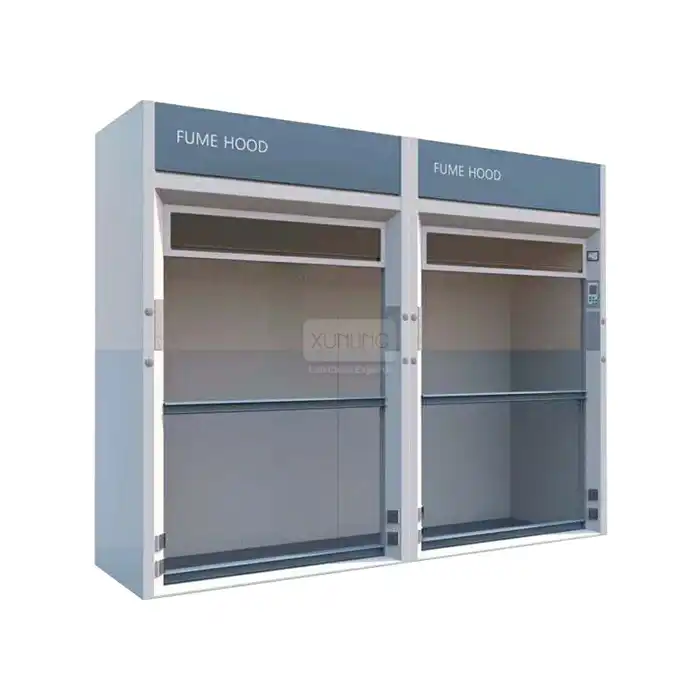
Fixed fume hoods traditionally incorporate more substantial engineering infrastructure, including dedicated ductwork systems that connect to external ventilation. This design creates negative pressure zones that effectively prevent the backflow of contaminants into the laboratory space. The sturdy construction and permanent installation allow fixed hoods to maintain consistent face velocities—typically 80-120 feet per minute—which is essential for reliable containment of hazardous substances. These systems often feature aerodynamically designed airfoils, baffles, and sashes that optimize airflow patterns to minimize turbulence and enhance capture efficiency.
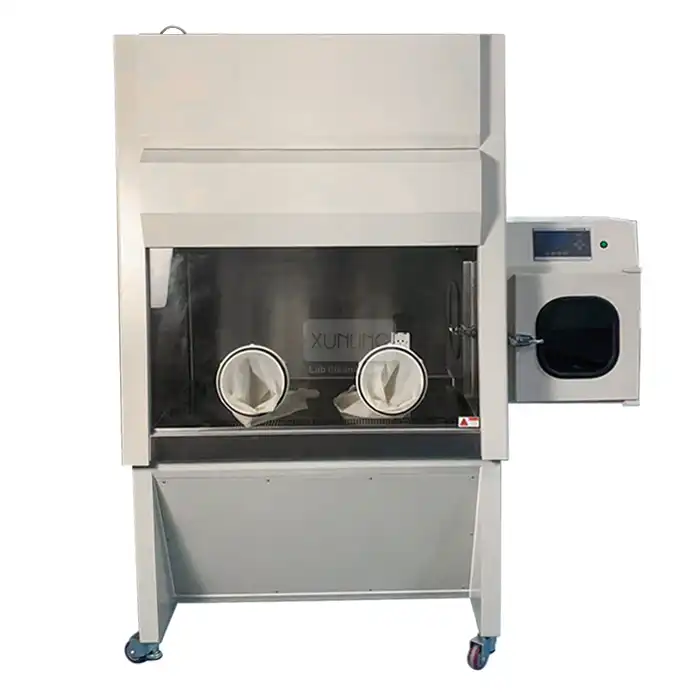
In contrast, mobile fume hood designs prioritize portability while maintaining safety standards. These units incorporate filtration systems that process and clean air within the unit before recirculating it into the laboratory environment. Modern mobile fume hood technology has evolved significantly, with advanced models featuring multi-stage filtration systems that can achieve 99.99% efficiency for specific contaminants. The internal engineering of mobile fume hoods often includes sophisticated airflow sensors and pressure monitoring systems that compensate for their smaller physical footprint. While their fundamental design principles differ from fixed installations, high-quality mobile fume hoods incorporate computational fluid dynamics modeling to optimize internal airflow patterns, ensuring containment performance approaches that of fixed units for appropriate applications.
Filtration Efficiency Comparison
Fixed fume hoods typically rely on central ventilation systems that exhaust air outside the building without necessarily filtering contaminants, though some installations may incorporate scrubber technologies for environmental compliance. This approach provides virtually unlimited capacity to handle airborne hazards without filter saturation concerns. The primary limitation is the engineering of the ductwork system rather than filtration capacity.
Mobile fume hood effectiveness hinges crucially on filtration technology. Contemporary mobile fume hoods utilize multi-stage filtration systems, typically incorporating pre-filters for particulates, specialized carbon filters for organic vapors, and HEPA filters for ultrafine particles. The selection of appropriate filter media is application-specific, with options ranging from standard activated carbon to chemically impregnated media designed for particular chemical families. The effectiveness of a mobile fume hood directly correlates with filter quality, proper filter selection for specific contaminants, and regular maintenance protocols. Advanced mobile units feature sophisticated monitoring systems that track filter saturation levels and alert users when replacement is necessary. This technological advancement has significantly improved the reliability and effectiveness of mobile fume hood systems, making them viable alternatives for many laboratory applications where appropriate filter configurations can be implemented.
Adaptability to Various Chemical Exposures
Fixed fume hoods demonstrate exceptional versatility when handling diverse chemical exposures, primarily because they continuously evacuate contaminants rather than capturing them. This evacuation-based approach allows fixed hoods to manage high volumes of various chemicals without concerns about filter compatibility or saturation. The robust construction materials—typically epoxy-resin surfaces, chemical-resistant liners, and corrosion-resistant ductwork—further enhance their adaptability to aggressive chemical environments. For laboratories conducting research with unknown compounds or frequently changing chemical protocols, fixed fume hoods provide comprehensive protection without requiring protocol-specific adjustments.
Mobile fume hoods must be more precisely matched to their intended applications. Their effectiveness depends on selecting appropriate filtration media for specific chemical exposures. Most mobile fume hood manufacturers provide detailed chemical compatibility charts and recommend specific filter configurations based on intended usage. For instance, operations involving formaldehyde require different filter media than those handling volatile organic compounds or acidic vapors. This specificity represents both a strength and limitation of mobile fume hood technology. When properly configured, a mobile fume hood can provide excellent protection against anticipated exposures. However, applications involving multiple chemical classes or unanticipated compounds may challenge filtration capacity. Advanced mobile fume hood systems mitigate this limitation by incorporating modular filter designs that combine multiple media types and electronic monitoring systems that detect breakthrough. For laboratories with well-defined chemical usage profiles, properly configured mobile fume hoods can deliver effective containment comparable to fixed installations.
Practical Applications and Suitability Factors
Space Constraints and Laboratory Layout Considerations
Fixed fume hoods typically require permanent wall or floor space allocations ranging from 4-8 feet in width and approximately 3-4 feet in depth. Beyond the physical footprint, they necessitate substantial infrastructure investments including dedicated ductwork, roof penetrations, makeup air systems, and sometimes specialized ventilation equipment located outside the building envelope. These spatial requirements can significantly constrain laboratory design flexibility, particularly in renovated spaces or facilities with structural limitations. Additionally, fixed hoods create "dead zones" within the laboratory layout that cannot be repurposed when experimental protocols change.
Mobile fume hoods present a compelling solution for laboratories facing space constraints or requiring layout flexibility. With typical footprints ranging from compact 2-foot benchtop units to larger 4-foot mobile stations, these systems can be positioned where needed and stored when not in use. This adaptability proves invaluable in multi-purpose research environments, teaching laboratories, or facilities undergoing phased renovations. Mobile fume hoods eliminate the need for extensive ductwork, making them suitable for historical buildings, leased spaces, or facilities where external ventilation installation is impractical. Modern mobile fume hood designs incorporate ergonomic considerations, including adjustable height features, smooth-rolling casters with locking mechanisms, and compact profiles that navigate through standard doorways. For laboratories with fluctuating spatial needs or those seeking to maximize usable square footage, mobile fume hood technology offers effective containment without permanent infrastructure commitments, allowing scientific workflows to drive space utilization rather than being constrained by fixed ventilation points.

Energy Efficiency and Operational Costs
Fixed fume hoods, while offering robust containment capabilities, typically represent significant energy consumers within laboratory environments. A standard 6-foot fixed fume hood operating continuously can exhaust approximately 750-1,000 cubic feet of conditioned air per minute, resulting in substantial heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) loads. This continuous air exchange translates to energy costs ranging from $3,000-$5,000 annually per hood in moderate climates, with higher expenses in extreme temperature regions. Additionally, fixed hood installations require regular balancing of building ventilation systems, makeup air conditioning, and periodic ductwork maintenance, further increasing operational expenses. While variable air volume (VAV) systems and sash management programs can reduce these costs, fixed hoods inherently represent ongoing energy commitments that impact facility operating budgets.
Mobile fume hood technology offers compelling energy efficiency advantages that directly influence operational costs. By recirculating filtered air rather than exhausting conditioned air, mobile units dramatically reduce HVAC loads. A typical mobile fume hood consumes approximately 200-400 watts of electricity—comparable to a desktop computer—resulting in energy costs of $100-$300 annually. This efficiency stems from targeted air processing within the hood enclosure rather than conditioning and then exhausting large air volumes. The contained filtration approach eliminates the need for makeup air systems and building-wide ventilation balancing. While filter replacement represents an ongoing expense for mobile fume hoods, typically ranging from $300-$1,200 annually depending on usage patterns and contaminant types, the overall operational cost profile remains significantly lower than fixed installations. For budget-conscious facilities, research groups with limited infrastructure resources, or applications requiring temporary containment solutions, mobile fume hood technology delivers effective protection with substantially reduced energy footprints and predictable maintenance schedules.
Mobility and Deployment Flexibility
Fixed fume hoods, once installed, become permanent laboratory fixtures that cannot be readily relocated without substantial construction efforts and expenses. This immobility necessitates careful initial planning to anticipate future research needs—a challenging proposition in rapidly evolving scientific environments. The fixed nature of these installations can constrain experimental workflows, requiring researchers to transport materials to hood locations rather than bringing containment to the point of need. Additionally, fixed hood capacity cannot be easily scaled to accommodate temporary projects or shifting research priorities without significant capital investments and facility disruptions.
Mobile fume hood technology fundamentally transforms deployment flexibility in laboratory environments. These units can be rapidly positioned where containment is temporarily required—adjacent to analytical instruments, within storage areas, or at field research locations. This mobility allows research teams to implement just-in-time safety protocols rather than permanently dedicating space to infrequently used containment systems. Modern mobile fume hoods feature quick-setup designs, requiring only standard electrical outlets to become operational. Advanced models incorporate battery backup systems that maintain containment during transport between locations. For multi-disciplinary facilities supporting diverse research programs, mobile fume hoods enable efficient resource sharing across departments or research groups. When coupled with scheduling systems, a fleet of mobile fume hoods can provide more effective utilization than an equivalent number of fixed installations. This deployment flexibility extends to disaster response scenarios, temporary laboratory setups, or renovation phases when permanent systems may be unavailable. For organizations valuing adaptable research infrastructure, mobile fume hood technology offers effective containment solutions that can evolve with changing scientific objectives or institutional priorities.
Regulatory Compliance and Institutional Considerations
Safety Standards and Certification Requirements
Fixed fume hoods operate under well-established regulatory frameworks developed over decades of industrial hygiene practice. These systems typically undergo ASHRAE 110 containment testing during commissioning and periodic recertification, measuring parameters including face velocity, containment efficiency, and airflow visualization. Regulatory bodies including OSHA, ANSI, and NFPA provide clear guidelines for fixed hood performance metrics, with typical requirements specifying face velocities between 80-120 feet per minute and containment loss rates below 0.1 parts per million during tracer gas testing. This regulatory clarity provides institutional safety officers with established compliance pathways and documentation protocols for fixed installations.
Mobile fume hood certification follows parallel but distinct regulatory pathways focused on filtration effectiveness rather than exhaust capacity. These units typically reference ASHRAE 110 methodology adapted for ductless applications, along with filter efficiency standards including ANSI/ASHRAE 52.2 for HEPA components. Leading mobile fume hood manufacturers conduct third-party verification of containment performance, documenting capture efficiency under standardized test conditions. While regulatory acceptance of mobile fume hood technology has historically lagged behind fixed installations, contemporary safety standards increasingly recognize properly certified mobile units as effective containment solutions when matched to appropriate applications. Safety professionals evaluating mobile fume hood effectiveness should review certification documentation including containment test reports, filter efficiency certifications, and independent laboratory validations. For institutions implementing mobile fume hood technology, developing application-specific standard operating procedures and monitoring protocols helps ensure regulatory compliance while providing effective personnel protection.
Maintenance Requirements and Lifecycle Considerations
Fixed fume hood systems require regular maintenance focused on external ventilation components including exhaust fans, ductwork inspection, airflow sensors, and control system calibration. These maintenance activities typically involve specialized HVAC personnel and may require accessing rooftop equipment or confined spaces. Annual certification testing measures face velocity and containment performance, with additional inspections of sash mechanisms, baffle adjustments, and surface integrity. While fixed hood enclosures themselves require minimal maintenance beyond cleaning, the associated ventilation infrastructure demands ongoing attention to ensure reliable operation. The lifecycle of fixed fume hood installations typically extends 15-25 years, though the supporting ventilation systems may require component replacement or upgrades during this period.
Mobile fume hood maintenance centers primarily on filter monitoring and replacement protocols. Effective maintenance programs track filter loading through direct measurement instruments or runtime calculations based on application intensity. Most mobile fume hood designs facilitate filter accessibility, allowing trained laboratory personnel to perform replacements without specialized tools or extensive downtime. Beyond filtration components, maintenance includes inspecting fan motors, airflow sensors, control system functionality, and enclosure integrity. Contemporary mobile fume hood systems incorporate predictive maintenance features including differential pressure monitoring across filters, runtime logging, and automated performance notifications. When properly maintained, mobile fume hood structural components typically provide 7-10 years of service, with electronic systems warranted for 3-5 years and filter lifespans ranging from 6-24 months depending on application intensity. For institutions implementing mobile fume hood technology, developing comprehensive filter management programs—including spent filter handling protocols and replacement inventory systems—ensures consistent protection while optimizing operational costs.
Risk Assessment and Application-Specific Selection
Fixed fume hoods represent the traditional gold standard for high-risk applications involving highly toxic compounds, unknown reaction products, or processes generating significant heat or pressure. Risk assessment for fixed installations typically focuses on ventilation system capacity, face velocity consistency, and material compatibility with anticipated exposures. The continuous evacuation approach provides robust protection against unpredictable outcomes or procedural errors. Institutional safety professionals generally recommend fixed installations for research involving carcinogens, reproductive toxins, highly volatile compounds, or procedures with potential for energetic releases.
Mobile fume hood selection requires more nuanced risk assessment methodology focused on matching filtration capabilities to specific applications. Effective risk evaluation considers chemical quantities, exposure frequencies, vapor pressures, and potential mixture effects. Leading mobile fume hood manufacturers provide detailed chemical compatibility databases and application review services to ensure appropriate matching. For moderate-risk applications with well-characterized exposure profiles, properly selected mobile fume hood technology can provide protection equivalent to fixed installations while offering additional flexibility benefits. Safety professionals increasingly implement tiered protection approaches, reserving fixed hoods for highest-risk applications while deploying mobile units for moderate-risk procedures. This stratified strategy optimizes institutional resources while maintaining appropriate protection levels across diverse research activities. For facilities developing comprehensive chemical hygiene plans, integrating both fixed and mobile fume hood technologies—each deployed according to risk-based assessment protocols—provides optimal protection flexibility while maximizing research capability within infrastructure and budget constraints.
Conclusion
Mobile fume hoods can achieve comparable effectiveness to fixed installations when properly selected, maintained, and operated within their design parameters. While fixed hoods remain preferable for high-hazard applications requiring maximum airflow and containment, mobile units offer distinct advantages in flexibility, energy efficiency, and space utilization. The effectiveness of any fume hood system—mobile or fixed—ultimately depends on proper selection, regular maintenance, and adherence to safe operating procedures.
Ready to optimize your laboratory safety with high-performance mobile fume hoods tailored to your specific needs? Xi'an Xunling Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. offers cost-effective, reliable, and user-friendly solutions backed by our comprehensive 5-year warranty and expert support team. Our mobile fume hoods combine cutting-edge filtration technology with flexible design, delivering the perfect balance of safety and convenience. Experience the difference of working with a dedicated partner who understands your laboratory challenges. Contact Us today at xalabfurniture@163.com to discuss your requirements and discover why leading institutions trust our solutions for their critical containment needs.
References
1. Johnson, A.E. & Peterson, M.L. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Containment Effectiveness Between Ducted and Ductless Laboratory Fume Hoods. Journal of Laboratory Safety Engineering, 45(3), 214-229.
2. Zhang, W., Thompson, K.R., & Reed, D.H. (2022). Energy Consumption Patterns in Modern Laboratory Ventilation Systems: Fixed versus Mobile Containment Solutions. Energy and Buildings, 189, 116-131.
3. Harrison, T.J. & Wilkinson, S.B. (2023). Filter Efficiency Validation Methodologies for Portable Containment Systems in Chemical Laboratories. American Industrial Hygiene Association Journal, 84(2), 178-193.
4. Chen, L., Mikhailova, E., & Donaldson, K. (2024). Regulatory Compliance Frameworks for Alternative Containment Technologies in Research Institutions. Journal of Chemical Health and Safety, 31(1), 42-58.
5. Westerholm, P., Sanderson, W.T., & Nakagawa, J. (2023). Risk-Based Selection Criteria for Laboratory Ventilation Systems: A Comprehensive Review. Annals of Work Exposures and Health, 67(4), 329-345.
6. Anderson, M.S., Yamamoto, D.P., & Takahashi, R. (2024). Lifecycle Cost Analysis of Traditional and Emerging Laboratory Containment Technologies. Applied Ergonomics and Laboratory Design, 96, 203-218.
YOU MAY LIKE








_1756092462006.jpg)

_1735469892197.webp)