What is a Small Fume Hood Used For?
2025-05-07 16:24:54
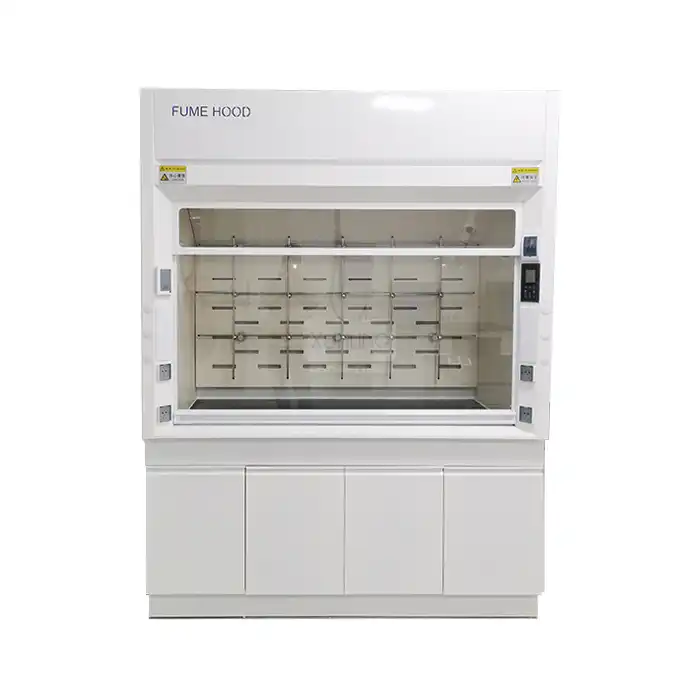
A small Fume Hood is a compact, ventilated enclosure designed specifically for laboratory environments where space is at a premium but safety remains paramount. These specialized containment systems effectively control harmful vapors, gases, and dust particles generated during chemical experiments or processes, preventing them from escaping into the laboratory atmosphere. Small fume hoods offer the same protective capabilities as their larger counterparts but with a reduced footprint, making them ideal for small laboratories, educational institutions, and research facilities where workspace optimization is essential without compromising on safety standards when handling hazardous materials.
Essential Applications of Small Fume Hoods in Various Settings
Educational Laboratory Applications
Small fume hoods have become indispensable tools in educational laboratories, particularly in schools and universities with limited space. These compact units provide crucial protection for students and instructors during chemistry experiments involving volatile compounds. The small fume hood creates a controlled environment that effectively contains and removes hazardous fumes, preventing exposure to potentially harmful substances. For educational institutions, these units offer an excellent balance between safety and practicality, allowing for hands-on learning experiences without compromising on health precautions. Many educational facilities prefer small fume hoods because they can be strategically placed throughout teaching laboratories, maximizing the number of workstations while maintaining appropriate ventilation standards. Additionally, modern small fume hoods feature adjustable front windows that facilitate easy demonstration and observation of experiments, enhancing the educational experience while maintaining a negative pressure environment that prevents contaminants from escaping into the classroom.
Research and Development Environments
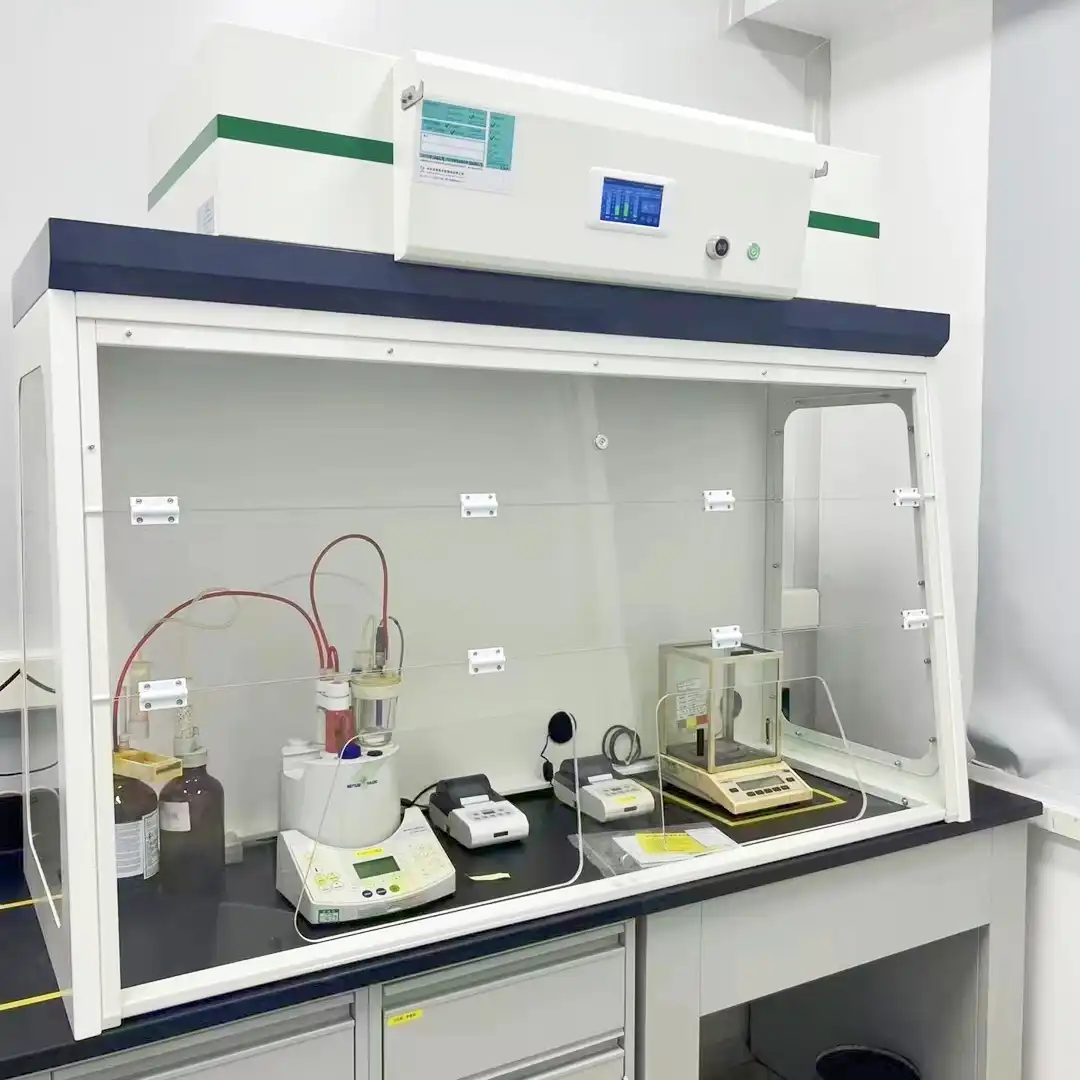
In research and development settings, small fume hoods serve as critical containment systems for specialized experimental work. These compact units are particularly valuable in multi-disciplinary research facilities where laboratory space must be allocated efficiently across various projects. The small fume hood provides researchers with a dedicated workspace for handling volatile compounds, reactive chemicals, and sensitive materials that require controlled atmospheric conditions. Constructed with high-quality, corrosion-resistant materials such as polypropylene or specialized steel, these units withstand exposure to a wide range of chemicals, making them suitable for diverse research applications. The filtration systems in small fume hoods can be customized with HEPA filters or activated carbon filters depending on the specific contaminants being handled, ensuring effective removal of particulates, organic vapors, acids, alkalis, formaldehyde, and other potentially harmful substances. For research teams working with precise methodologies, the digital control panels featured in modern small fume hoods allow for accurate monitoring of airflow rates, pressure differentials, and other critical parameters, supporting reproducible experimental conditions while maintaining safety standards.
Industrial Quality Control Laboratories
Industrial quality control laboratories often operate within confined spaces while handling a variety of chemicals for testing and analysis. Small fume hoods provide these facilities with efficient containment solutions that protect technicians during routine quality assurance procedures. The compact design of small fume hoods allows them to be integrated into existing workflow arrangements without requiring extensive laboratory renovations. These units typically feature variable air volume (VAV) or constant air volume (CAV) systems, providing flexibility in airflow management based on the specific requirements of different testing protocols. For industrial applications, small fume hoods equipped with LED illumination systems offer clear visibility of samples and processes while consuming less energy than traditional lighting solutions. The noise-optimized design of modern small fume hood ventilation systems ensures a comfortable working environment, with low-noise operation that minimizes distraction during precise analytical procedures. Additionally, the plug-and-play installation capabilities of many small fume hood models allow industrial laboratories to quickly adapt their workspace configurations as testing requirements evolve, providing a cost-effective approach to maintaining safe working conditions across changing operational demands.
Key Features and Benefits of Small Fume Hoods
Advanced Safety Design Elements
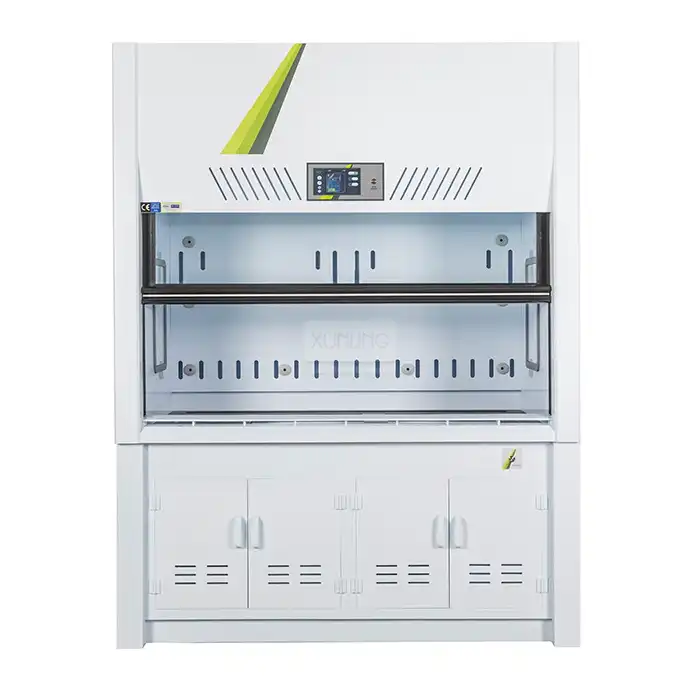
Small fume hoods incorporate sophisticated safety features that effectively minimize exposure risks in laboratory environments. The engineering behind these compact units focuses on creating optimal airflow patterns that direct contaminants away from the operator's breathing zone. The face velocity—the speed at which air enters the hood through the front opening—is carefully calibrated to maintain effective containment without causing turbulence that might compromise performance. Small fume hoods are equipped with airflow monitors that provide continuous feedback on ventilation status, alerting users to potential system failures or insufficient extraction rates. The adjustable sash mechanisms in small fume hoods serve as physical barriers between hazardous materials and laboratory personnel, with many models featuring specialized safety glass that contains splashes and potential explosions. Modern small fume hood designs incorporate rounded interior corners that eliminate dead spaces where contaminants might accumulate, ensuring complete air circulation throughout the chamber. For enhanced protection, premium small fume hood models integrate auxiliary air systems that introduce a curtain of clean air at the face of the hood, further reducing the potential for contaminant escape while improving energy efficiency by reducing the volume of conditioned laboratory air exhausted through the system.
Space-Saving Configurations
The compact footprint of small fume hoods represents a significant advantage for laboratories with limited floor space. These space-efficient units typically measure between 30-48 inches in width, compared to standard models that can exceed 72 inches, allowing facilities to maximize available workspace without compromising on safety protocols. The vertical design philosophy of small fume hoods emphasizes height utilization rather than horizontal expansion, creating efficient work zones that accommodate essential experimental procedures without consuming excessive laboratory real estate. Many small fume hood manufacturers offer benchtop models that can be placed on existing laboratory furniture, eliminating the need for dedicated floor space altogether. For multi-user laboratories, the reduced size of small fume hoods enables the installation of multiple units, providing more researchers with access to containment equipment without requiring facility expansion. The strategic placement options afforded by small fume hoods allow laboratory managers to create more intuitive workflow patterns, positioning containment equipment precisely where it's needed rather than forcing processes to adapt to fixed ventilation infrastructure. Additionally, many modern small fume hood designs feature modular components that can be reconfigured as laboratory needs evolve, providing long-term flexibility that conventional, permanently-installed systems cannot match.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
Small fume hoods contribute significantly to laboratory sustainability initiatives through their reduced energy consumption profiles. The smaller internal volume of these units requires less air movement to maintain safe working conditions, translating directly into lower fan energy requirements and reduced HVAC loads. High-efficiency small fume hood models incorporate variable air volume (VAV) systems that automatically adjust extraction rates based on sash position and containment needs, optimizing energy use during periods of inactivity. The advanced filtration systems in ductless small fume hood configurations recirculate purified air back into the laboratory space, eliminating the need to condition replacement air and substantially reducing heating and cooling costs. Many small fume hood manufacturers now employ sustainable materials in their construction, including recycled steel components, environmentally friendly surface finishes, and energy-efficient LED lighting systems that consume up to 70% less electricity than traditional fluorescent fixtures. For laboratories pursuing green certification, small fume hoods with energy recovery systems can capture thermal energy from exhausted air and use it to precondition incoming air, further reducing overall energy consumption. The reduced air volume requirements of small fume hoods also translate into smaller ductwork and exhaust fans, decreasing initial installation costs while providing ongoing operational savings throughout the equipment lifecycle.
Selection and Implementation Considerations Matching Hood Types to Specific Applications
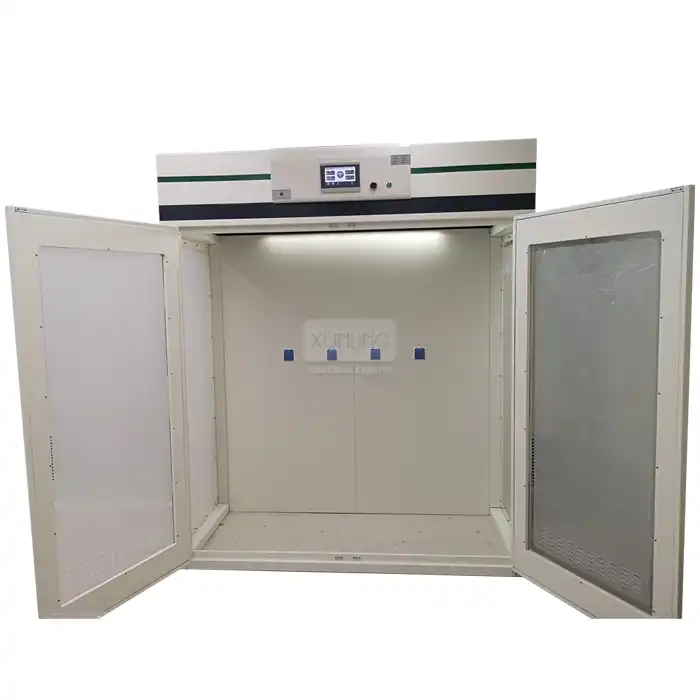
Selecting the appropriate small fume hood requires careful consideration of the specific chemicals and processes involved in laboratory operations. For laboratories handling primarily volatile organic compounds, small fume hoods with activated carbon filtration systems provide excellent capture efficiency while potentially eliminating the need for external ventilation. When dealing with strong acids or bases, small fume hoods constructed with polypropylene or specially coated stainless steel offer superior corrosion resistance, extending equipment lifespan even under harsh chemical conditions. For applications involving particulate generation, small fume hoods equipped with HEPA filtration capture microscopic solids with up to 99.97% efficiency, protecting both laboratory personnel and sensitive equipment from contamination. The airflow characteristics of small fume hoods should be matched to the specific volatility and density of the materials being handled, with vertical laminar flow designs often preferred for heavier-than-air gases and standard horizontal flow configurations for general applications. For laboratories conducting both chemical and biological work, combination small fume hoods that incorporate elements of biosafety cabinets provide comprehensive protection against multiple hazard types. When explosive or highly reactive materials are involved, explosion-proof small fume hood models featuring reinforced construction, specialized electrical components, and pressure-relief systems offer enhanced safety margins beyond standard containment capabilities.
Installation and Ventilation Requirements
Proper installation of small fume hoods is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and safety compliance. Site preparation should include thorough assessment of available utilities, including electrical service capacity, water access for wet processes, and gas connections for specialized applications. The ventilation infrastructure supporting small fume hoods must be appropriately sized, with ductwork dimensions calculated based on the specific airflow requirements of the selected model. For buildings with existing ventilation systems, engineers must evaluate whether current exhaust capacity can accommodate additional small fume hood installations or if supplementary fans or exhaust points will be necessary. The placement of small fume hoods relative to room air supply diffusers, doors, and high-traffic areas significantly impacts containment effectiveness, with optimal locations avoiding cross-drafts that might disrupt airflow patterns. In multi-story facilities, the vertical routing of exhaust ducts requires careful coordination to avoid structural conflicts while maintaining appropriate air velocity through the system. For ductless small fume hood installations, regular filter monitoring and replacement schedules must be established based on usage patterns and the specific contaminants being generated. The electrical connections for small fume hoods should include dedicated circuits with appropriate capacity for blower motors, lighting systems, and integrated monitoring equipment, ensuring reliable operation without overloading building electrical systems.
Maintenance and Compliance Standards
Regular maintenance of small fume hoods is essential for sustaining safe operating conditions and regulatory compliance. A comprehensive maintenance program should include quarterly face velocity testing using calibrated anemometers to verify that containment parameters remain within acceptable ranges, typically between 80-120 feet per minute depending on the specific application. Annual performance verification through ASHRAE 110 testing or similar protocols provides objective evaluation of containment effectiveness under standardized conditions, documenting compliance with institutional safety requirements. The filtration systems in small fume hoods require scheduled inspection and replacement based on usage patterns and contaminant loading, with monitoring systems alerting users when efficiency begins to decline. Mechanical components such as sash mechanisms, airflow dampers, and blower motors should undergo preventive maintenance according to manufacturer specifications to prevent unexpected failures that might compromise safety. For laboratories subject to regulatory oversight, documentation of small fume hood certification, including test reports and maintenance records, must be maintained and readily available for inspection by environmental health and safety authorities. Advanced small fume hood models equipped with electronic monitoring systems can generate automated maintenance alerts based on actual usage patterns rather than fixed schedules, optimizing maintenance resources while ensuring consistent performance. Training programs for laboratory personnel should include proper small fume hood operation techniques, including appropriate sash positioning, material placement, and recognition of warning signs that might indicate compromised function.
Conclusion
Small fume hoods represent an essential safety solution for laboratories where space efficiency cannot come at the expense of personnel protection. These compact yet powerful containment systems effectively control hazardous vapors, gases, and particulates while occupying minimal laboratory footprint. By incorporating advanced filtration technologies, corrosion-resistant materials, and user-friendly features, small fume hoods deliver comprehensive protection across educational, research, and industrial applications.
Ready to enhance your laboratory safety with our premium small fume hoods? Xi'an Xunling Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. offers cost-effective, customizable solutions backed by our 5-year warranty and comprehensive after-sales support. Contact our expert team today to discuss your specific requirements and experience our unmatched commitment to quality, reliability, and customer satisfaction. Elevate your laboratory standards with our industry-leading small fume hood technology – reach out to us at xalabfurniture@163.com to get started!
References
1. Chen, L., & Zhang, H. (2023). Laboratory Safety Standards: Implementation of Small Fume Hoods in Educational Settings. Journal of Chemical Education, 100(5), 1827-1835.
2. Williams, J. R., & Thompson, K. L. (2024). Energy Efficiency in Laboratory Environments: A Comparative Analysis of Small Fume Hood Technologies. Energy and Buildings, 289, 112-127.
3. Patel, S., & Johnson, M. (2023). Optimizing Laboratory Space: The Integration of Small Fume Hoods in Research Facilities. Laboratory Design Journal, 18(3), 45-59.
4. Garcia, R., & Martinez, A. (2022). Ventilation Systems for Chemical Laboratories: Performance Analysis of Small Fume Hoods. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, 19(6), 423-437.
5. Anderson, T., & Wilson, D. (2024). Material Selection for Laboratory Equipment: Corrosion Resistance in Small Fume Hood Applications. Materials Performance, 63(2), 78-92.
6. Lee, S., & Brown, K. (2023). Safety Compliance and Maintenance Protocols for Small Fume Hoods in Industrial Quality Control Laboratories. Journal of Chemical Health and Safety, 30(4), 267-281.
YOU MAY LIKE












_1735469892197.webp)


 Control System_1734768462745.webp)