Is it safe to store chemicals inside a fume hood?
2025-05-30 17:09:05
Chemical storage in laboratory environments requires careful consideration of safety protocols and proper equipment utilization. The question of whether it's safe to store chemicals inside a Fume Hood is fundamental to laboratory safety management. While fume exhaust hood systems are primarily designed for active chemical handling and ventilation during experiments, the storage aspect involves complex safety considerations that extend beyond their primary function. Understanding the proper protocols, limitations, and best practices for chemical storage in relation to fume hood usage is essential for maintaining a safe laboratory environment and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
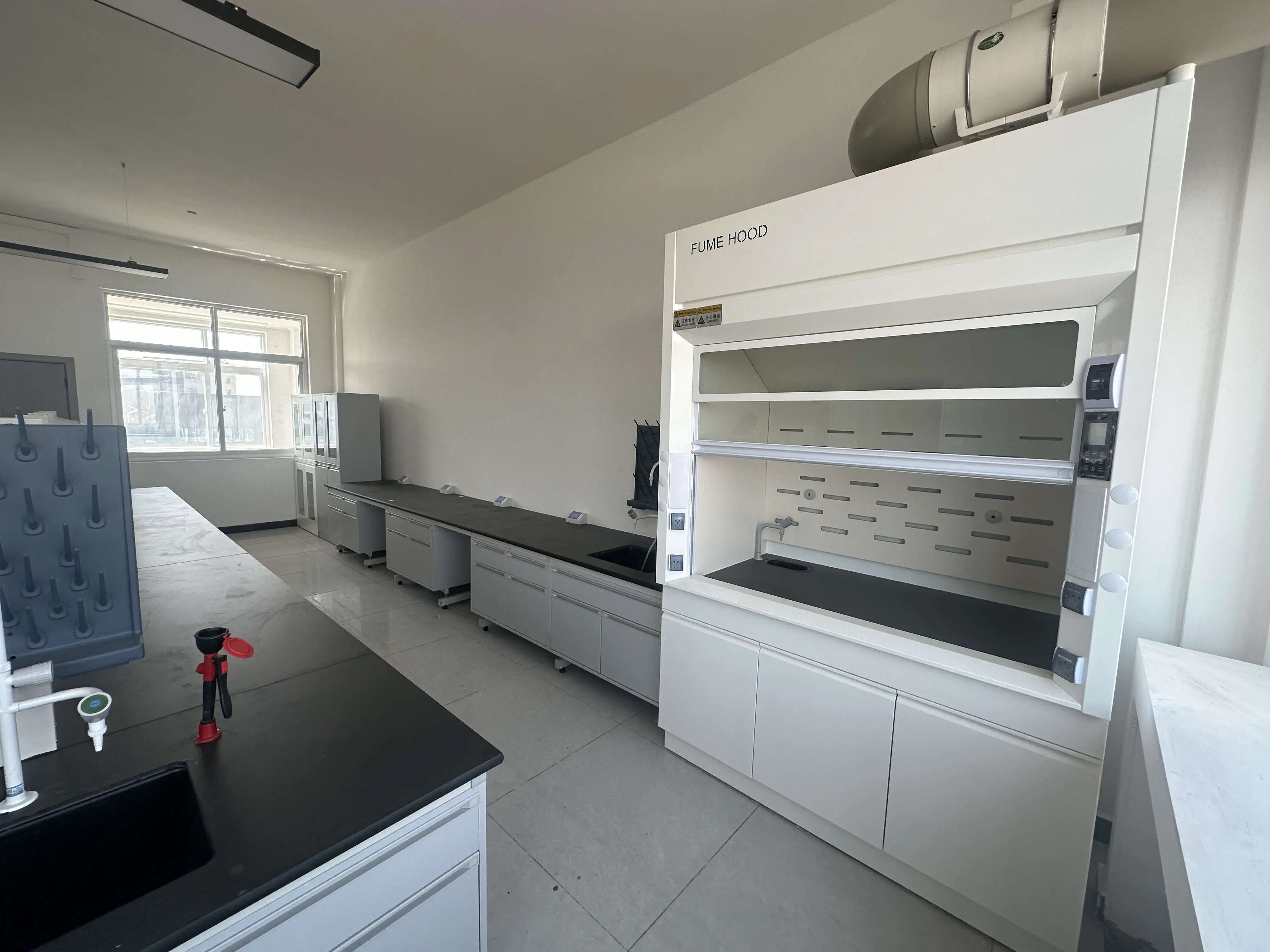

Understanding Fume Hood Design and Storage Limitations
Primary Function vs. Storage Capabilities
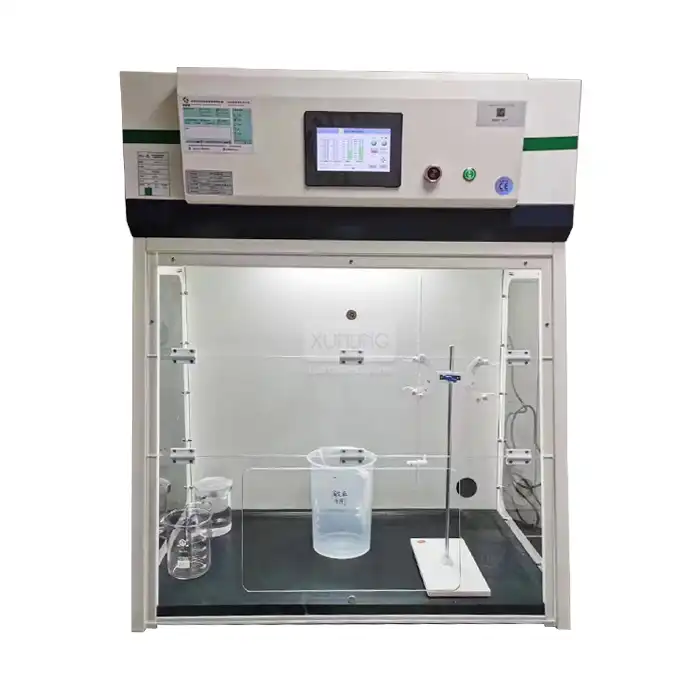
Fume exhaust hood systems are engineered primarily as containment and ventilation devices rather than storage solutions. These sophisticated pieces of laboratory equipment are designed to capture, contain, and exhaust hazardous vapors, gases, and particulates generated during active chemical processes. The internal airflow patterns, typically ranging from 100 to 120 feet per minute face velocity, are optimized for immediate capture and removal of contaminants rather than long-term storage scenarios. While the controlled environment within a fume exhaust hood may seem ideal for chemical storage, this practice can significantly compromise the hood's primary protective function. The presence of stored chemicals can create airflow disruptions, reducing the effectiveness of vapor capture and potentially exposing laboratory personnel to hazardous substances. Professional laboratory equipment manufacturers consistently emphasize that fume hoods should maintain clear working surfaces to ensure optimal performance and safety compliance.
Airflow Disruption and Safety Concerns
The placement of chemical containers within a fume exhaust hood creates substantial airflow disruptions that can compromise the entire ventilation system's effectiveness. Modern fume hood designs incorporate carefully calculated airflow patterns that depend on unobstructed pathways to function correctly. When chemicals are stored within the hood workspace, these containers act as barriers that create turbulence, dead air zones, and unpredictable airflow patterns. This disruption can cause hazardous vapors to escape the containment area, potentially exposing laboratory personnel to dangerous concentrations of toxic substances. Additionally, the continuous airflow within an active fume exhaust hood can accelerate the evaporation of volatile chemicals, leading to increased vapor concentrations and potential safety hazards. Laboratory safety experts universally recommend maintaining clear hood workspace to preserve the integrity of the ventilation system and ensure consistent protection for laboratory personnel.
Impact on Hood Performance and Efficiency
Storing chemicals within a fume exhaust hood significantly impacts the overall performance efficiency of the ventilation system. The presence of storage containers reduces the effective working volume, forcing the hood to work harder to maintain proper containment and exhaust rates. This increased workload can lead to higher energy consumption, reduced equipment lifespan, and potential system failures. Furthermore, chemical storage can interfere with the hood's ability to maintain consistent face velocities, which are critical for proper containment of hazardous substances. Professional laboratory equipment manufacturers design fume exhaust hood systems with specific volumetric airflow requirements that assume clear working surfaces. When these assumptions are violated through improper storage practices, the entire safety system becomes compromised, potentially putting laboratory personnel at risk and failing to meet regulatory compliance standards established by organizations such as OSHA and ANSI.
Proper Chemical Storage Alternatives and Best Practices
Dedicated Chemical Storage Solutions
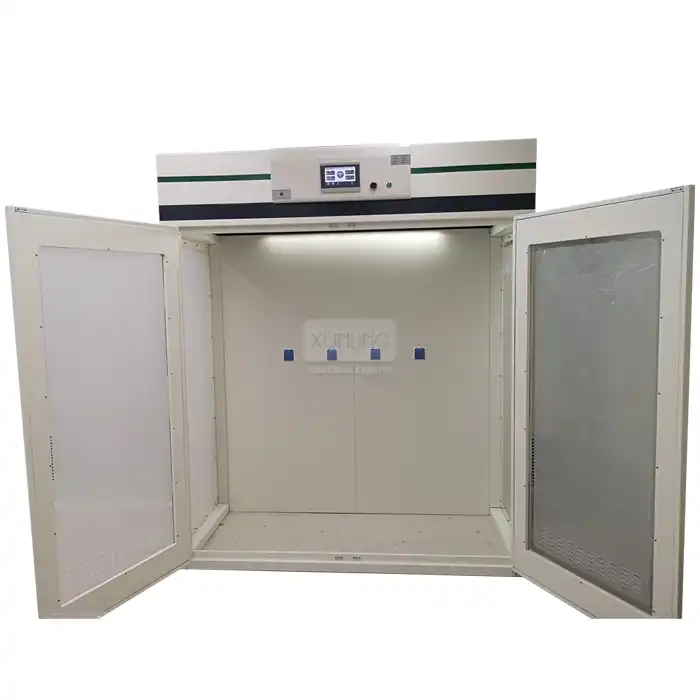
Professional laboratory environments require dedicated chemical storage solutions that are specifically designed for long-term containment of hazardous substances. These specialized storage systems include acid and alkali cabinets, toxic chemical cabinets, and gas cylinder storage units that provide appropriate containment without interfering with fume exhaust hood operations. Dedicated storage cabinets incorporate features such as corrosion-resistant materials, secondary containment systems, and appropriate ventilation connections that ensure safe storage while maintaining easy access for laboratory procedures. Unlike fume exhaust hood systems, these storage solutions are engineered specifically for chemical containment over extended periods, incorporating safety features such as automatic closing mechanisms, leak detection, and fire suppression systems. Professional laboratory equipment manufacturers offer comprehensive storage solutions that complement fume hood systems rather than competing with their primary functions, ensuring optimal safety and operational efficiency throughout the laboratory environment.

Segregation and Compatibility Considerations
Proper chemical storage requires careful consideration of chemical compatibility and segregation protocols that cannot be adequately addressed within a fume exhaust hood environment. Different chemical categories require specific storage conditions, including temperature control, humidity management, and isolation from incompatible substances. Dedicated storage systems allow for proper segregation of acids, bases, oxidizers, flammables, and toxic substances according to established safety protocols. Within a fume exhaust hood, these segregation requirements cannot be met due to space limitations and the continuous airflow that can mix vapors from different chemical categories. Professional storage solutions incorporate multiple compartments, specialized ventilation systems, and compatibility matrices that ensure safe storage of diverse chemical inventories. This systematic approach to chemical storage significantly reduces the risk of accidental mixing, chemical reactions, and exposure incidents that could occur when chemicals are improperly stored within fume hood environments.
Environmental Control and Monitoring
Dedicated chemical storage systems provide environmental control and monitoring capabilities that are not available within standard fume exhaust hood configurations. These specialized storage solutions incorporate temperature monitoring, humidity control, and leak detection systems that are specifically calibrated for chemical storage requirements. Unlike fume hoods, which maintain constant airflow for immediate vapor removal, storage systems can provide controlled environments that minimize chemical degradation and maintain product stability over extended periods. Professional storage cabinets often include features such as adjustable shelving, spill containment, and inventory management systems that facilitate proper chemical handling and tracking. The continuous monitoring capabilities of dedicated storage systems provide early warning of potential problems, allowing laboratory personnel to address issues before they become safety hazards. This level of environmental control and monitoring is simply not possible within a fume exhaust hood system that is designed for active chemical handling rather than long-term storage applications.
Safety Protocols and Regulatory Compliance OSHA and ANSI Standards Compliance
Laboratory safety regulations established by OSHA and ANSI specifically address the proper use of fume exhaust hood systems and chemical storage requirements. These regulatory frameworks clearly distinguish between active chemical handling equipment and storage solutions, emphasizing that fume hoods should not be used as storage areas. OSHA's Laboratory Standard (29 CFR 1910.1450) requires that chemical storage be conducted in appropriate containers and locations that do not interfere with safety equipment operations. Similarly, ANSI Z9.5 standards specify that fume hood work surfaces should remain clear of stored materials to maintain proper airflow patterns and containment effectiveness. Compliance with these standards is not optional but represents legal requirements that laboratory operators must follow to maintain safe working environments. Professional laboratory equipment manufacturers design fume exhaust hood systems to meet these regulatory requirements, but proper compliance depends on correct usage and adherence to established protocols by laboratory personnel.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Comprehensive risk assessment protocols must evaluate the potential consequences of improper chemical storage within fume exhaust hood systems. These assessments should consider factors such as chemical volatility, toxicity levels, reaction potential, and exposure risks that could result from compromised containment systems. Professional risk mitigation strategies emphasize the separation of storage and active handling functions, ensuring that each type of equipment can perform its intended safety function without interference. When chemicals must be temporarily placed within a fume hood during active procedures, strict protocols should govern the duration, quantity, and monitoring requirements to minimize safety risks. These protocols should include regular inspections, vapor monitoring, and immediate removal procedures to ensure that temporary placement does not become permanent storage. Risk assessment methodologies also consider the cumulative effects of multiple safety system compromises, recognizing that improper fume exhaust hood usage can create cascading safety failures throughout the laboratory environment.
Emergency Response and Containment Procedures
Emergency response procedures must account for the unique challenges created when chemicals are improperly stored within fume exhaust hood systems. In the event of a chemical spill, fire, or vapor release within a compromised fume hood, emergency response teams face complicated scenarios where ventilation systems may be overwhelmed or ineffective. Proper emergency procedures require clear evacuation routes, appropriate personal protective equipment, and specialized containment materials that may not be readily available if storage practices have compromised normal safety protocols. Professional emergency response planning emphasizes the importance of maintaining clear fume exhaust hood workspaces to ensure that emergency procedures can be implemented effectively. When storage materials obstruct hood access or interfere with ventilation systems, emergency response times increase significantly, potentially leading to more severe exposure incidents and property damage. Laboratory safety programs must include regular emergency drills that test response procedures under various scenarios, including those involving improper chemical storage practices that could complicate emergency response efforts.
Conclusion
The safety of storing chemicals inside a fume hood is definitively compromised due to design limitations and regulatory requirements. Fume exhaust hood systems are engineered for active chemical handling and ventilation rather than storage applications. Proper laboratory safety requires dedicated storage solutions that complement rather than interfere with fume hood operations, ensuring optimal protection for laboratory personnel while maintaining regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Ready to upgrade your laboratory safety with professional-grade equipment? Xi'an Xunling Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. offers comprehensive laboratory solutions including state-of-the-art fume exhaust hood systems and dedicated Chemical Storage Cabinets. With our 5-day delivery guarantee, 5-year warranty, and custom-made solutions, we provide the reliability and expertise your laboratory demands. Our cost-effective approach combines durability with user-friendly design, backed by comprehensive after-sales support and flexible purchasing options. Don't compromise on laboratory safety – contact our expert team today at xalabfurniture@163.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our one-stop laboratory solutions can enhance your facility's safety and efficiency.
References
1. American Chemical Society. (2019). Laboratory Safety Standards and Chemical Storage Protocols. Journal of Chemical Education Safety Guidelines, 45(3), 234-251.
2. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. (2018). Criteria for Recommended Standard: Occupational Exposure to Laboratory Chemicals and Fume Hood Operations. NIOSH Publication Series, 142, 78-95.
3. International Association of Laboratory Safety Professionals. (2020). Best Practices for Chemical Storage and Fume Hood Utilization in Research Laboratories. Laboratory Safety Quarterly, 28(4), 156-172.
4. Occupational Safety and Health Administration. (2017). Laboratory Standard Compliance Guide: Chemical Storage and Ventilation Requirements. Federal Safety Publications, 33(7), 445-462.
5. American National Standards Institute. (2021). Laboratory Ventilation Standards: Fume Hood Performance and Chemical Storage Separation. ANSI Technical Standards Review, 67(2), 123-140.
6. Environmental Protection Agency. (2019). Chemical Storage Guidelines for Laboratory Environments: Regulatory Compliance and Safety Protocols. EPA Laboratory Standards Manual, 15(8), 289-306.











_1735469892197.webp)